CE Marking - The Ultimate Guide (2024)
04/02/2023 Law & Legislation
This is the ultimate guide to CE marking for any importer, manufacturer or distributor that is selling products on the European market. I’ll not only cover the most asked questions, but I will also tell you how you can conduct most steps of the CE marking process yourself. So, if you want to make sure that you can legally sell your products on the market of the European Union, you’ll love this guide.
Table of contents
What is CE marking (the CE mark)?
What is the meaning of CE marking?
When is CE marking mandatory?
What products need CE marking?
What are the benefits of CE marking?
Which countries accept the CE mark?
What are the responsibilities of manufacturers, importers and distributors?
How do I get CE marking?
What does the CE marking process look like?
CE marking self-certification: When can I self-certify?
What are the CE certification costs?
Does Amazon require CE marking?
The CE marking logo (free download CE mark logo)
What is CE marking (the CE mark)?
CE marking is a marking on specific products indicating that the manufacturer declares compliance of that product with the relevant European product safety legislation.
What is the meaning of CE marking?
When a product is CE marked, it means that the manufacturer has verified compliance with the essential health and safety requirements as indicated in the applicable European directives and regulations.
By marking the product, the manufacturer takes full responsibility and liability over the product.
CE marking is found on many products that are traded within the European Economic Area (The EEA consists of all 27 EU countries and Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway).
The letters CE stand for Conformité Européenne, meaning European Conformity.
When is CE marking mandatory?
CE marking is mandatory for products that fall under one of the 25 CE directives or regulations. When a product is not covered by one of these directives or regulations, affixing the CE logo is forbidden. Often, more than one directive or regulation can be applicable to a product.
To determine if a directive or regulation applies to a product, consult the scope and the definitions of the directive. Also, check the exceptions that are not covered by the directive to find out if your product is excluded.
What products need CE marking?
Products that fall under the scope of the following directives and regulations require CE marking:
- Directive 2006/42/EC on machinery
- Directive 2000/14/EC on noise emission in the environment by equipment for use outdoors
- Regulation (EU) 2016/424 cableway installations
- Directive 2009/125/EC on ecodesign requirements for energy-related products
- Regulation (EU) 2016/426 on appliances burning gaseous fuels
- Directive 2009/48/EC on toy safety
- Directive 2011/65/EU on the restrictions of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical equipment
- Directive 2013/29/EU on pyrotechnic articles
- Directive 92/42/EEC on hot water boilers
- Directive 2014/28/EU on explosives for civil uses
- Directive 2014/29/EU on simple pressure vessels
- Directive 2014/30/EU relating to electromagnetic compatibility
- Directive 2014/31/EU on weighing instruments
- Directive 2014/32/EU on measuring instruments
- Directive 2014/33/EU on lifts
- Directive 2014/34/EU relating to equipment and protective systems for use in potentially explosive atmospheres
- Directive 2014/35/EU relating to the making available on the market of electrical equipment designed for use within certain voltage limits
- Directive 2014/53/EU relating to radio equipment
- Directive 2013/53/EU on recreational craft
- Directive 2014/68/EU on pressure equipment
- Regulation (EU) 2017/746 on in vitro diagnostic medical devices
- Regulation (EU) No 305/2011 on construction products
- Regulation (EU) 2017/745 on medical devices
- Regulation (EU) 2016/425 on personal protective equipment
- Regulation (EU) 2019/945 unmanned aircraft systems
CE marking is not required for products such as pharmaceuticals, chemicals, cosmetics and food.
Listen to these podcasts to learn more about:
What are the benefits of CE marking?
Products that comply with the CE marking requirements benefit from the following:
Free movement of goods
When your product meets the requirements, the product can move freely between the member states. The member states together operate as a single market. Within the single market, compliant products can be traded without any restrictions. As such, CE marking can be seen as a kind of passport for the European marketplace.
High level of health, safety and environmental protection
Products that comply have a high level of health, safety and environmental protection, as they meet the requirements of the European directives. When the manufacturer applied harmonised standards to comply with the requirements of the directives, he or she has taken account of the current state-of-the-art procedures with respect to health, safety and environmental protection. Consumers and users of CE marked products enjoy the same level of protection.
Which countries accept the CE mark?
CE marking basically is a set of rules for certain products that are sold within the European Economic Area (EEA). The EEA consists of all 27 EU countries plus Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway.
The EU countries are:
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
The EEA creates a single European market, which allows free movement of goods, capital, services and people between its member states.
Switzerland is neither an EU nor an EEA member but is part of the single market. This means that CE products can be sold in Switzerland.
Also, Turkey is neither a member of the EU nor part of the EEA. However, as Turkey has fully implemented most of the European CE marking directives, the de facto situation means that CE marked products can be sold freely in Turkey.
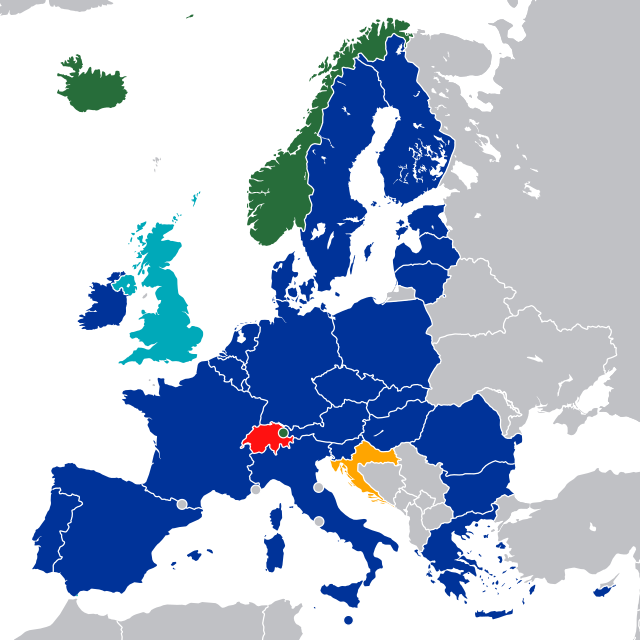
Countries that accept the CE mark (image from csiassoc.com)
What is the responsibility of a manufacturer, importer or distributor?
It is the responsibility of the person that places a product on the European market that the product is meeting the requirements of the CE marking directives and/or regulations.
So who is this person exactly?
It can be the manufacturer, the importer, or the distributor. All three may have different responsibilities.
A manufacturer is any natural or legal person who places a product on the EU market under his/her name or trademark, regardless of whether someone manufactures a product or has a product designed and/or manufactured by others.
The manufacturer is responsible for completing the CE marking process and thus making sure that the product complies with the relevant European legislation.
A manufacturer from outside the EU may appoint an authorised representative, or work with an importer.
What are the importer’s responsibilities?
An importer that imports a product from outside the EU is responsible for making sure that the product complies before placing it on the market.
An importer needs to make sure that the manufacturer from outside the EU has fulfilled all obligations, such as completing the CE marking conformity assessment procedure, compiling the technical file, and drafting the declaration of conformity.
As importers are considered to be producers under the product liability directive, they are fully liable for the products that they place on the European market.
Let’s look at an example.
We hear quite often that an importer thinks that a product complies because the non-European manufacturer has sent him a declaration of conformity.
It is the responsibility of the importer to verify that the product is meeting the requirements by checking the completeness, compliance and authenticity of the FULL technical documentation.
When an importer thinks that the product which they have placed on the market does not conform to European legislation, they must directly bring that product into conformity, withdraw it or recall it.
What about distributors?
A distributor is any natural or legal person in the supply chain, such as a retailer or wholesaler, who makes products available on the market.
A distributor buys a product from a manufacturer, importer, or other distributors. They have to be aware of the regulations and know which products should be CE marked and what the requirements on the language, labelling, packaging, and user instructions are.
It is their responsibility not to supply products that ‘they know or should have assumed, on the basis of information in their possession and as a professional', are not in compliance with the legislation.
Also note that when a distributor or an importer modifies a product or markets it under their own name, they are legally seen as the manufacturer and take over all responsibilities.
How do I get CE marking?
Do you want to know how to get CE marking? There are several ways to obtain this...
Of course you can outsource the entire CE process, but there is something that many people do not know.
And that is that this marking in principle is a self-certification process. Only for a few products is it required to test and certify your product by a notified body (NoBo).
This means that for most products you don’t need a NoBo. In these cases you can still outsource parts of the process and work with a CE expert (not to be confused with a NoBo), have only the tests done by a testing lab (also not to be confused with a NoBo), or do everything yourself, when you have the right equipment of course.
Let’s put this clearly in an overview:
| notified body | Only needed when required by certain directives and for certain product groups. |
| testing lab | Can help you conduct tests such as flammability test (for toys), EMC test or low voltage test. |
| CE consultants | Can guide you through the entire CE process, contact suppliers, determine if certification by a third party (NoBo) is required, conduct a risk analysis (if required), etc. |
| technical documentation agency | Supports you with creating the user and product safety instructions. |
A common mistake that is made
Be aware of this often encountered mistake…
Sometimes I hear that people don´t want to get a CE certificate or say that they don’t need to do CE marking, because they already have a CE certificate from their manufacturer.
This is wrong!
The CE certificate that manufacturers often claim to have is ‘just’ a test report, such as an EMC report or LVD report. That is just one of the required technical documents that is involved in the conformity assessment procedure (step 4), and which should be included in the technical file (step 5).
Other people mistake the declaration of conformity for a CE certificate. This is not the correct name. Also, be aware that the declaration of conformity should always be signed by the person that places the product on the European market.
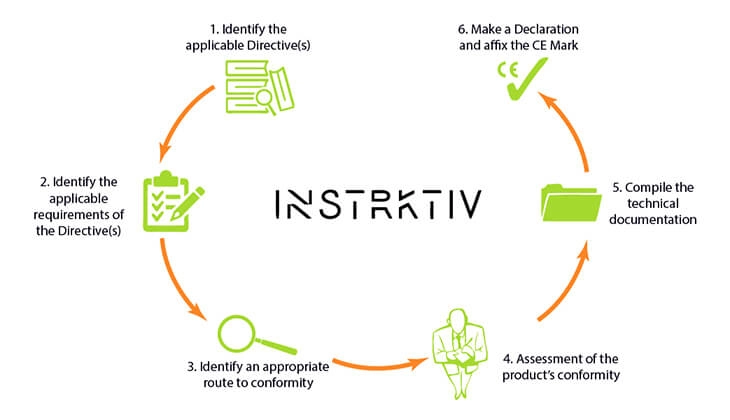
What does the CE marking process look like?
The CE marking process consists of the following 6 steps:
- Identify the applicable legislation and harmonised standards.
- Verify product specific requirements (see Step 2 of the CE marking process).
- Identify whether an independent conformity assessment (by a notified body) is necessary (see CE marking self- certification: When can I self-certify?).
- Conduct the conformity assessment.
- Draw up and keep available the required technical file.
- Affix the CE marking and draw up the EU declaration of conformity.
Have a look here for a more comprehensive description of the process.
CE marking self-certification: When can I self-certify?
We can describe self certification as ‘conducting the CE marking process without the requirement to have the assessment done by a notified body’.
Because in more than 90% of the cases, CE marking is a self-certification process.
Only for some directives it is required to let a notified body (NoBo) test and certify your product, to ensure compliance with the relevant essential requirements. This means that for most products you don’t need a NoBo, and self-certification is allowed.
Also, when a directive requires testing, it does not always mean that this needs to be done by a NoBo. Theoretically, you often can do it by yourself on the condition that you have the correct equipment and knowledge of the testing process.
To find out if you can self-certify your product:
- Identify the applicable directives.
- Download the applicable directives.
- Press Ctrl + f and search for ‘conformity assessment’ to find out if the CE marking is fully self-certifiable or if a NoBo is required.
Example 1: Low voltage directive
When we search (Ctrl + f) the low voltage directive for ‘conformity assessment’, we find the following provision, making clear that the conformity assessment procedure can be conducted by the manufacturer, and thus the CE marking is a self-certification process:
The manufacturer, having detailed knowledge of the design and production process, is best placed to carry out the conformity assessment procedure. Conformity assessment should therefore remain solely the obligation of the manufacturer. There is no conformity assessment procedure in this directive which requires the intervention of a notified body.
Example 2: Medical device regulation
When we search (Ctrl + f) the medical device regulation for ‘conformity assessment’, we find the following provision, making clear that the conformity assessment procedure for class I medical devices can be conducted by the manufacturer (and thus the CE marking is a self-certification process) but that for other classes a NoBo is required:
The conformity assessment procedure for class I devices should be carried out, as a general rule, under the sole responsibility of manufacturers in view of the low level of vulnerability associated with such devices. For class IIa, class IIb and class III devices, an appropriate level of involvement of a notified body should be compulsory.
Directives (and regulations) for which a NoBo is required include the ATEX directive, the medical devices regulation, the directive for pressure equipment, the simple pressure vessels directive and the gas appliance directive.
In some cases, self certification is only allowed if the manufacturer uses a harmonised standard, for example to comply with the requirements of the machinery directive and toy directive.
DO YOU NEED SUPPORT IN THE PROCESS OF CE MARKING?
We will support you in the process of CE marking to ensure your user instructions and technical documentation meet the legal requirements.
What are the CE certification costs?
That is a very tough question to answer, but let's give it a try.
CE certification costs can vary from below $100 to over $100,000. The CE marking costs totally depend on the kind of product and the certification procedure to be followed.
The certification procedure, or procedures, that apply is based on the intended use and the technical specifications of a product.
As 90% of all products can be certified without a notified body (NoBo), in many cases you won’t need third-party testing. This will be a massive cost saver.
As quite a lot of conformity assessments are visual inspections, without the need of special testing equipment, these visual checks can be done by yourself.
When you build your technical file yourself, and when you can conduct all testing yourself, you will also save quite a lot of money.
When you outsource the testing, without the need of a NoBo, you will at least have to pay for the testing costs.
Also, some testing might have been done by the supplier or by the manufacturer of components. In those cases, a certain amount of testing can be skipped sometimes, after validation of the supplier’s documentation.
For example, when you manufacture a product that contains a Bluetooth module that already has been tested and CE approved, you don't need to do the testing all over again.
The possible costs of CE marking in an overview:
- CE consultant
- General guidance/support
- Determining directives and standards
- Conformity assessment
- Compiling the technical file
- Checking compliance and completeness of technical files/test reports done by the manufacturer
- Risk analysis
- Testing done by the testing lab
- Notified body for conformity assessment
- Creating the user manual
A testing lab might charge you just 100 Euro to test if a toy complies with a certain standard. Certification of a complete production line can cost over 100,000 Euro.
The time that consultants, testing labs or notified bodies need to spend on your product and/or technical documentation will determine the largest part of the total cost of CE marking. Do you think that more than a day is needed for testing, conformity assessment, risk analysis, compiling the technical file, etc? Then multiply the estimated hours with a reasonable hourly fee of a legal expert, to conclude that the cost of CE marking is likely to exceed 1,500 Euro .
In order to determine the exact costs of CE marking, you first need to determine the following:
- Which CE directives or regulations apply to your product?
- Which (harmonised) standards apply to your product?
- Which certification procedures apply to your product?
Once this is known, you can collect and compare quotes from test laboratories, consultants, notified bodies and user manual service providers.
Does Amazon require CE marking?
E-commerce platforms in general, and specifically Amazon, are more and more taking your responsibilities seriously when it comes to product safety. Why?
Because when, for example, you import products from Asia and sell them on Amazon, you are fully responsible for making sure that your products comply with all mandatory product safety requirements.
These include requirements on the packaging, labelling, technical documentation and declaration of conformity.
The person or company that places a product on the European market, and not the supplier, is responsible for the product.
Certain products are classified by Amazon as requiring “pre-approval”. Product groups that need pre-approval include, but are not limited to, kitchen equipment, toys, lighting, batteries and chargers.
For these product groups, Amazon requires you to upload the declaration of conformity before the product can be sold.
A team of Amazon’s product compliance experts will then manually check if your declaration complies with the European requirements.
Make sure you have completed the full CE marking process before you draft and sign the declaration of conformity.
By signing the declaration, you declare that the product meets all European requirements and you will be held liable for the product.
You should take the following steps:
- Identify applicable directives and standards.
- Identify all applicable requirements.
- Determine if third-party testing is needed.
- Conduct the conformity assessment.
- Create the technical file.
- Draw up and sign the declaration of conformity
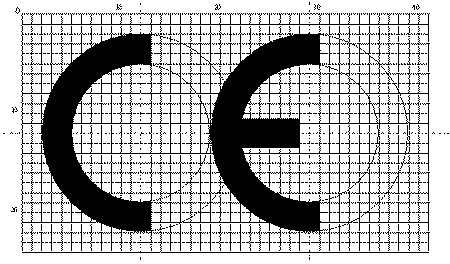
The CE marking logo (free download CE mark logo)
The last step of the CE marking process is affixing the CE mark to the product.
The individual directives have requirements on the CE mark. In general you should make sure that:
- The initials ‘CE’ are in the standard, predefined form.
- The CE marking has a height of at least 5 millimetres.
- The CE marking is placed onto the product or onto its data plate. When the size of the product does not allow this, the marking can be placed onto the packaging or in accompanying documents, such as the user manual.
- The CE marking is easily visible, readable and permanent.
Download the CE mark logo here.
Conclusion
So, do you want to CE certify your products to sell on the European market?
In this article I have discussed some of the most relevant CE marking topics.
By now you should know whether CE marking is mandatory for your product. You know where you can sell your product as soon as you comply and what your responsibilities are.
To sum up, in order to sell your product legally on the European market, you should follow the steps of the CE marking process.
For more information, listen to this podcast on How to CE mark a product.
Still need help? Hit the button below to contact us.
Resources:
 |
Ferry Vermeulen is a technical communication and compliance expert. He also is a parttime trainer at the Dutch standardisation institute (NEN). Listen to the INSTRKTIV podcast on Spotify or read one of his latest blog articles. Linkedin I Spotify I YouTube I Facebook I Twitter |
DO YOU NEED SUPPORT IN THE PROCESS OF CE MARKING?
We will support you in the process of CE marking to ensure your user instructions and technical documentation meet the legal requirements.
